The Complex Relationship Between the Federal Reserve and Mortgage Rates Explained
There is a common misconception that the Federal Reserve has complete control over mortgage rates. In reality, the Federal Reserve only influences mortgage rates, with the actual determination being made by the bond market. The Fed oversees the Fed Funds rate, representing the overnight lending rate for banks and setting the tone for the short end of the yield curve.
When rates at the short end of the yield curve rise, it impacts longer-duration rates as well. Investors demand higher interest rates for longer-dated Treasury bonds to justify locking in their money when short-term returns are attractive. The bond market ultimately evaluates the Federal Reserve’s decisions, leading to various yield curve scenarios.
It is important to note that mortgage rates are closely tied to the 10-year Treasury bond yield rather than the Fed Funds rate.
Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates
In early 2022, the Federal Reserve began a series of interest rate hikes in response to rising inflation, which peaked at 9.1%. As a result, mortgage rates saw a significant increase. Various factors contributed to the rise, with adjustments in Federal Reserve policy rates accounting for half of the movement.
Other factors, such as changes in the Term premium, prepayment risk, Option-Adjusted-Spread (OAS), lender fees, and inflation, also played a role in the increase in mortgage rates.

While it is challenging to quantify the exact impact of these factors on mortgage rates, estimates suggest a clear influence on rate movements.
Forecasting Mortgage Rate Declines
Analysts predict that a 25 basis points cut in the Fed’s rates could lead to a 12.5 basis points reduction in mortgage rates. If the Fed implements consecutive rate cuts, mortgage rates could potentially decrease further based on other contributing factors like inflation expectations and economic confidence.
Recent expectations for Fed Funds Rates hint at potential rate cuts, with projections indicating a modest decline in mortgage rates by the end of 2024 and 2025. Despite these reductions, the overall economic outlook suggests that mortgage rates may remain elevated for some time.

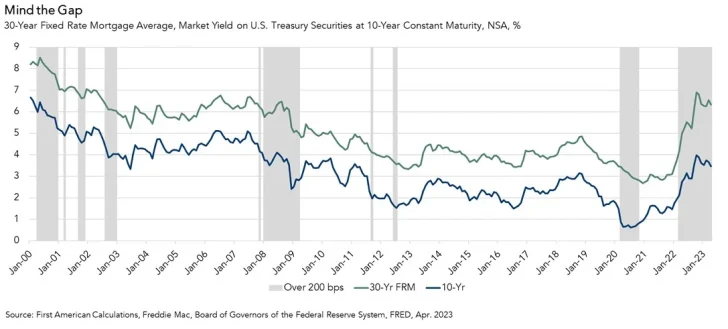
Potential Impact of Mortgage-Treasury Spread
The spread between the average 30-year mortgage rate and the 10-year Treasury rate, known as the Mortgage-Treasury Spread, could narrow in the future. While economic uncertainty widened the spread in recent years, current trends suggest a gradual decline back towards historical averages.
Challenges in Raising Mortgage Rates
Despite potential economic growth, significant challenges exist in raising mortgage rates further. Factors such as high inflation, market valuations, and government debt levels pose hurdles to aggressive rate hikes. The Federal Reserve must carefully navigate interest rate adjustments to avoid disrupting the economy.

Managing Expectations About Mortgage Rate Trends
For prospective homebuyers expecting a rapid decline in mortgage rates, it is essential to temper expectations. The Fed’s impact on rates is limited, and any significant changes will take time to materialize. Understanding the complex factors influencing rates can help individuals make informed decisions about real estate investments.
Have questions or suggestions about the Federal Reserve’s influence on mortgage rates? Share your thoughts in the comments below. And if you’re in the market for a mortgage, consider checking rates on Credible to find competitive offers from a network of lenders.

